Transistor এর শ্রেনী বিভাগ কর।
উত্তরঃ Transistor
একটি অর্ধপরিবাহী বা সেমিকন্ডাক্টর ডিভাইস যার ভিতর দিয়ে বিদ্যুৎ প্রবাহিত
করলে তার আউটপুটে সেই প্রবাহ বর্ধিত আকারে পাওয়া যায় এবং বৈদ্যুতিক সুইচ
হিসাবে ব্যবহার করা হয় তাকে Transistor বলে।

Transistor
এর তিনটি পা থাকে যাকে ইমিটার(Emmitar), বেস(Base) ও কালেক্টর(Collector)
বলে। এর একটি পা এর মধ্যদিয়ে প্রবাহিত অল্প পরিমাণ কারেন্ট বা ভোল্টেজ
নিয়ন্ত্রনের মাধ্যমে অন্য দুটি পা দিয়ে প্রবাহিত উচ্চ মানের কারেন্ট বা
ভোল্টেজকে নিয়ন্ত্রন করা হয়।


Transistor সাধারণত দুই প্রকারঃ
- Bi-Polar Junction Transistor(BJT) ----> 1. PNP & 2. NPN
- Field Effect Transistor (FET)
Field Effect Transistor (FET) দুই প্রকারঃ
- Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
- Metal Oxid Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) দুই প্রকারঃ
- N-Type
- P-Type
Metal Oxid Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) দুই প্রকারঃ
- Deplection Mode
- Enhancement Mode
Deplection Mode & Enhancement Mode উভয়ই দুই প্রকারঃ
- N - Channel
- P - Channel

Types of Transistors
As
mentioned earlier, on a broader scale, the major families of
Transistors are BJTs and FETs. Irrespective of the family they belong
to, all Transistors have proper / specific arrangement of different
semiconductor materials. Commonly used semiconductor materials for
manufacturing transistor are Silicon, Germanium and Gallium-Arsenide.
Basically,
the transistors are classified depending on their structure. Each type
of transistors has their own characteristics, advantages and
disadvantages.
Physically
and structurally speaking, the difference between BJT and FET is that
in BJT both majority and minority charge carriers are required to
operate, whereas in case FETs, only majority charge carriers are
required.
Based
on their properties and characteristics, some transistors are primarily
used for switching purpose (MOSFETs) and on the other hand, some are
transistors are used for amplification purpose (BJTs). Some transistors
are designed for both amplification and switching purposes.
Junction Transistors
Junction
Transistors are generally called as Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT).
The term ‘Bipolar’ means both electrons and holes are required for
conducting current and the term ‘Junction’ means it contain PN Junction
(two junctions, in fact).
The
BJTs have three terminals named Emitter (E), Base (B) and Collector
(C). The BJT transistors are classified in to NPN and PNP transistors
depending on the construction.
BJTs
are essentially current-controlled devices. If small amount of current
flows through the base of a BJT transistor, then it causes a flow of
large current from emitter to collector. The Bipolar Junction
Transistors have low input impedance and it causes to flow large current
through the transistor.
The
Bipolar Junction Transistors are only turned ON by the input current,
which is given to the base terminal. BJTs can operate in three regions.
They are:
- Cut-off
Region: Here the transistor is in ‘OFF’ state i.e., the current flowing
through the transistor is zero. It is basically an open switch.
- Active Region: Here the transistor acts as an amplifier.
- Saturation Region: Here the transistor is in fully ‘ON’ state and also works as a closed switch.
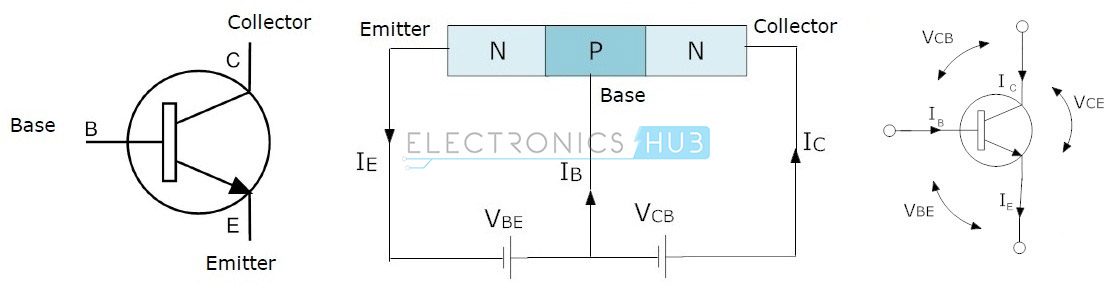
NPN Transistor
NPN
is one of the two types of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT). The NPN
transistor consists of two n-type semiconductor materials and they are
separated by a thin layer of p-type semiconductor. Here, the majority
charge carriers are electrons while holes are the minority charge
carriers. The flow of electrons from emitter to collector is controlled
by the current flow in the base terminal.
A
small amount of current at base terminal causes a large amount current
to flow from emitter to collector. Nowadays, the more commonly used
bipolar transistor is NPN transistor, because the mobility of electrons
is greater than mobility of holes. The standard equation for the
currents flowing in the transistor is
IE = IB + IC
The symbols and structure for NPN transistors are given below.
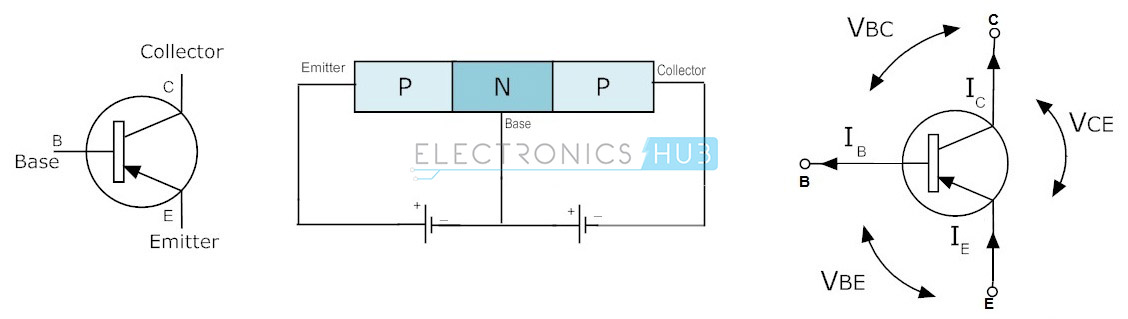
PNP Transistor
The
PNP is another type of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT). The PNP
transistors contain two p-type semiconductor materials and are separated
by a thin layer of n-type semiconductor. The majority charge carriers
in the PNP transistors are holes while electrons are minority charge
carriers. The arrow in the emitter terminal of transistor indicates the
flow of conventional current. In PNP transistor, the current flows from
Emitter to Collector.
The
PNP transistor is ON when the base terminal is pulled LOW with respect
to emitter. The symbol and structure for PNP transistor is shown below.
FET (Field Effect Transistor)
The
Field-Effect-Transistor (FET) is another major type of transistor.
Basically, the FET also have three terminals (like BJTs). The three
terminals are: Gate (G), Drain (D) and Source (S). Field Effect
Transistor are classified into Junction Field Effect transistors (JFET)
and Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistors (IG-FET) or Metal Oxide
Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFET).
For
the connections in the circuit, we also consider a fourth terminal
called Base or Substrate. The FETs have control on the size and shape of
a channel between Source and Drain, which is created by voltage applied
at Gate.
The
Field Effect Transistors are uni-polar devices, as they require only
the majority charge carriers to operate (unlike BJT, which are bipolar
transistors).
JFET (Junction-Field Effect Transistor)
The
Junction-Field-Effect transistor (JFET) is an earliest and simple type
of Field Effect Transistor. The JFETs are used as switches, amplifiers
and resistors. This transistor is a voltage-controlled device. It
doesn’t need any biasing current.
The
voltage applied between gate and source controls the flow of electric
current between source and drain of the transistor. The JFET transistors
are available in both N–Channel and P–Channel types.
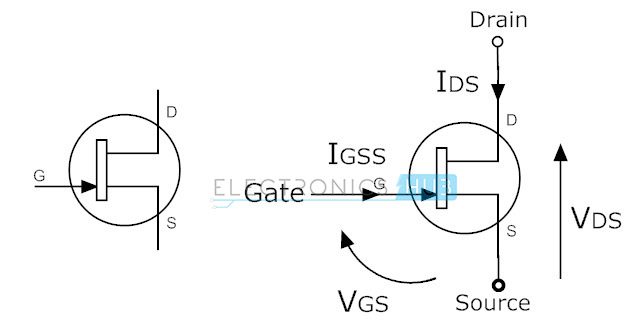
N–Channel JFET
In
N–Channel JFET, the current flow is due to the electrons. When voltage
is applied between gate and source, a channel is formed between source
and drain for current flow. This channel is called N–Channel. Nowadays,
N–Channel JFETs are preferable type than P–Channel JFET. The symbols for
N-channel JFET transistor are given below.
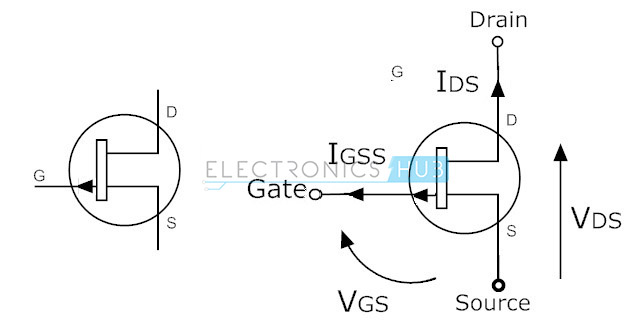
P–Channel JFET
In
this type of JFET, the current flow is because of holes. The channel
between source and drain is called P–Channel. The symbols for P–Channel
JFETs are given below. Here, the arrow marks indicate the direction of
current flow.
MOSFET
Metal
Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is most commonly
used and most popular type of among all transistors. The name ‘Metal
Oxide’ indicates that the Gate region and the channel are separated by a
thin layer of metal oxide (usually, SiO2).
Hence,
MOSFET is also known as Insulated Gate FET as the Gate region is
completely insulated from the Source – Drain region. There is an extra
terminal known as Substrate or Body, which is the main Semiconductor
(Silicon) in which the FET is fabricated. So, the MOSFET has four
terminals drain, source, gate and body or substrate.
MOSFET
has many advantages over BJT and JFET, mainly it offers high input
impedance and low output impedance. It is used in switching and power
circuits and it is a main component on Integrated Circuit designing
technologies.
The
MOSFET transistors are available in depletion and enhancement types.
Further, the depletion and enhancement types are classified into
N–Channel and P–Channel types.
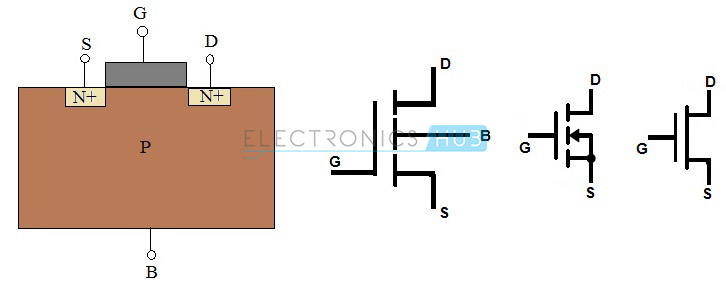
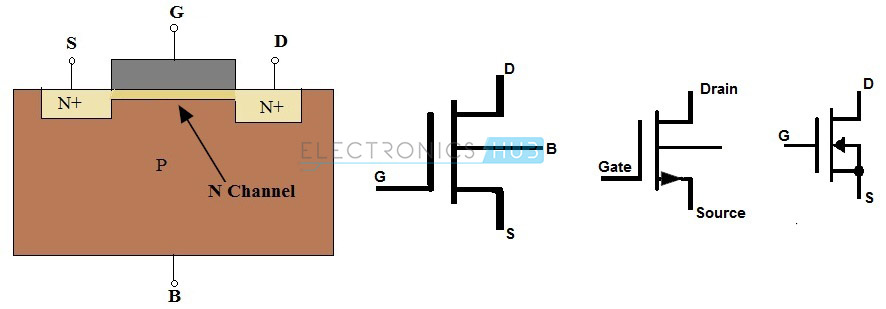
N-Channel MOSFET
The
MOSFET having N-channel region between source and drain is called
N-channel MOSFET. Here, the source and gate terminals are heavily doped
with n-type materials situated in a heavily doped p-type semiconductor
material (substrate).
The
current flow between source and drain is because of electrons. The gate
voltage controls the current flow in the circuit. N–Channel MOSFET is
most commonly used than P–Channel MOSFET because the mobility of
electrons is high than mobility of holes.
The symbols and structures for N–Channel MOSFET transistors are given below (both Enhancement and Depletion mode).
P–Channel MOSFET
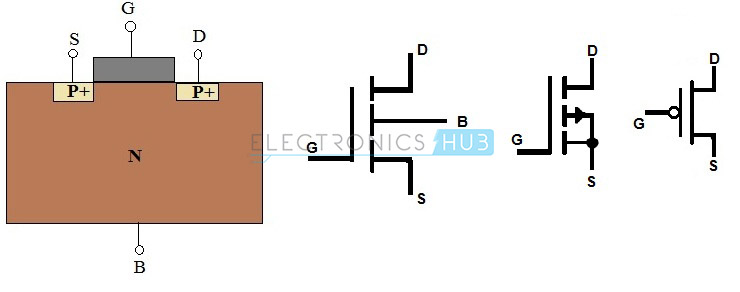
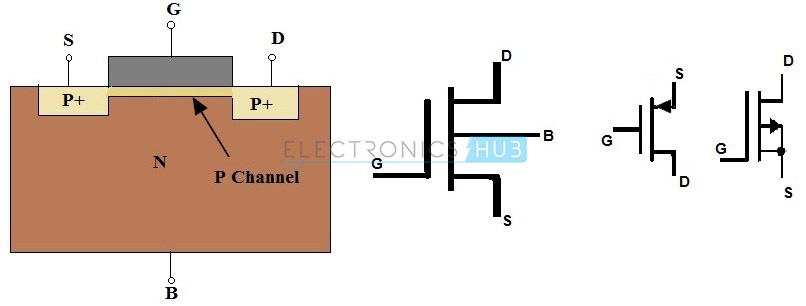
The
MOSFET having P–Channel region between source and drain is called as
P–Channel MOSFET. Here, the source and drain terminals are heavily doped
with P-type material and the substrate is doped with N-type material.
The current flow between source and drain is because of holes
concentration. The applied voltage at gate will controls the flow of
current through channel region.
The symbols and structures for P–Channel MOSFET transistors are given below (both Enhancement and Depletion mode).
Transistors Based on Function
Transistors
are also classified depending on the functions (operations or
applications) they perform. Different types of transistors based on
their function are explained below.
Small Signal Transistors
The
basic function of small signal transistors is to amplify small signals
but sometimes these transistors are also used for switching purpose.
Small signal transistors are available in market in the form of NPN and
PNP transistors. We can usually see some value printed on the body of
small signal transistor, which indicates the hFE of transistor.
Depending
on this hFE value, we can understand the capacity of transistor to
amplify the signal. The commonly available hFE values are the range of
10 to 500. The collector current value of these transistors is 80 to 600
mA. This type of transistors operates with the frequency range of 1 to
300 MHz. The name of the transistor itself indicates that these
transistors amplify small signals, which use small voltages and
currents, such as few milli volts and milli amperes of current.

Small
signal transistors are used in almost all types of electronic equipment
and also these transistors are used in several applications, some of
them are ON or OFF switches for general use, LED diode driver, Relay
driver, Audio mute function, Timer circuits, Infrared diode amplifier,
Bias supply circuits etc.
Small Switching Transistors
Small
switching transistors are those transistors which are primarily used
for switching but also sometimes for amplification. Like small signal
transistors, small switching transistors are also available in the form
of NPN and PNP and these types of transistors also have hFE values.
The
hFE value range for these transistors is from 10 to 200. At hFE value
200, the transistors are not good amplifiers but they act as better
switches. The collector current values range from 10 to 1000 mA. These
transistors are used mostly in switching applications.

Power Transistors
The
transistors which are used in the high-power amplifiers and power
supplies are called as Power Transistors. The collector terminal of this
transistor is connected to the base of a metal device and this
structure acts as heat sink which dissipates excess power for the
applications.
These
types of transistors are available in the form of NPN, PNP and
Darlington transistors. Here, the collector current values range from 1
to 100 A. The operating frequency range from 1 to 100 MHz. The power
values of these transistors are range from 10 to 300 W. The name of the
transistor itself indicates that the power transistors are used in the
applications where high power, high voltage and high current are
required.
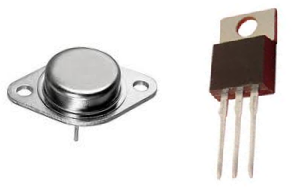
High Frequency Transistors
High
frequency transistors are used for small signals which operate at high
frequencies and these are used in high-speed switching applications.
High frequency transistors are also called as RF Transistors.
These transistors have maximum frequency values of about 2000 MHz. The collector current (IC)
value ranges from 10 to 600 mA. These types of transistors are also
available in the form of NPN and PNP. These are mainly used in the
applications of high frequency signals and also these transistors must
be ON or OFF at high speeds only. These transistors are used in HF, VHF,
UHF, CATV and MATV oscillator and amplifier circuits.

Photo Transistor
Photo
transistors are the transistors which operate depending on the light
i.e., these transistors are light sensitive. A simple photo transistor
is nothing but a bipolar transistor which contains light sensitive area
instead of the base terminal.
The
photo transistors have only 2 terminals instead of 3 terminals (in
BJTs). When the light sensitive area is dark, then no current flows in
transistor i.e., transistor is in OFF state.

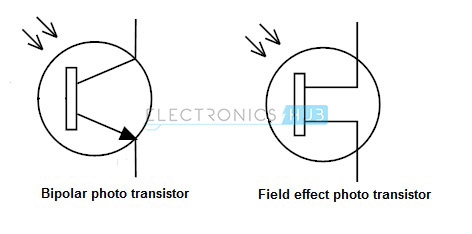
When
light sensitive area is exposed to light, then a small amount of
current generates at base terminal and it causes a large current to flow
from collector to emitter. The photo transistors are available in both
BJT and FET transistor types. These are named as photo-BJTs and
photo-FETs.
Unlike
photo-BJTs, the photo-FETs are generating gate voltage by using light,
which controls the current flow between drain and source terminals.
Photo-FETs are more sensitive to light than photo-BJTs. The symbols for
photo-BJT and photo-FETs are shown above.
Uni-Junction Transistors (UJT)

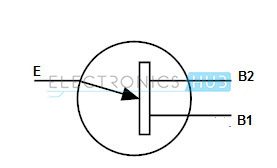
Uni-Junction
Transistors (UJT) are used only as electrically controlled switches.
These transistors do not contain any amplification characteristics
because of their design. These are generally three lead transistors, in
which, two are called as Base Terminals and the third is called the
Emitter.
Now,
let us see the operation of uni-junction transistor. If there is no
potential difference between emitter and any one of the base terminals
(B1 or B2), then a small amount of current flows between B1 and B2.
If
sufficient amount of voltage is applied to the emitter terminal, then a
high current is generated at emitter terminal and it adds to small
current between B1 and B2, which then causes a flow of large current in
the transistor.
Here,
the emitter current is the primary current source for controlling the
total current in the transistor. The current between the terminals B1
and B2 is very small and due to this reason, these transistors are not
suitable for amplification purpose.
উইকিপিডিয়া ও ইন্টারনেট হতে তথ্য, ছবি সংগৃহীত


























